Digitalising Education in Rural India
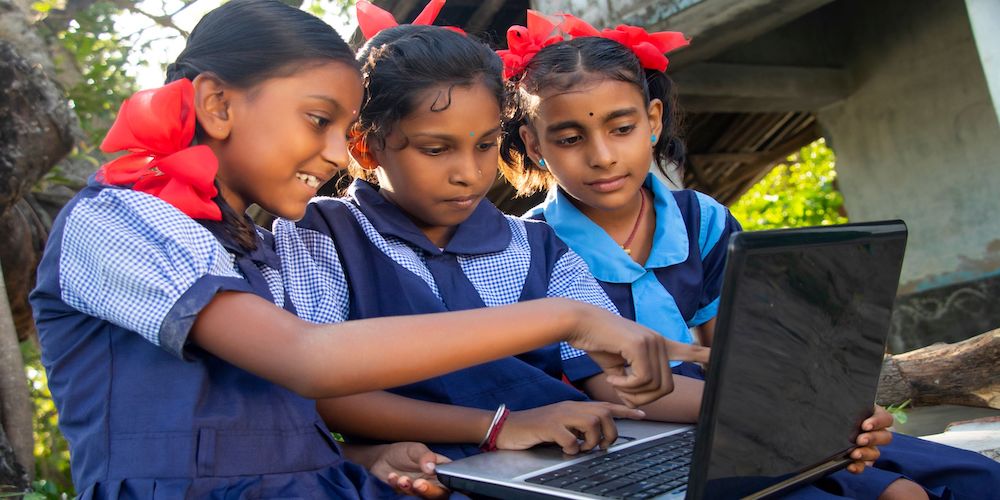

Technological inclusion at school level is crucial as technology is no longer a privilege, it is a necessity. It helps build future-readiness in students thereby widening their career choices and livelihood opportunities by preparing them to handle rapidly evolving market and skill needs.
School education in rural India has always struggled to keep up with its urban brethren. The problem has become all the more serious after the outbreak of the Corona pandemic struck.
Overnight, schools were forced to go online. Majority percentage of schools in India whether urban or rural struggled with digital deliveries as they were not 100% digitally enabled, some barely.
Thus, the pandemic induced need widened the digital gaps in the school system leading to huge learning gaps in the students. It became highly imperative therefore for all the schools to undergo rapid digital transformation. The challenge in rural India has been bigger as it is very difficult for millions of people in villages to have access to technology before they can begin to use it.
Experts say that here the role of the three key contributors (facilitators) is vital : Samaj (Society or Ecosystem), Sarkar (Government), and Bazar (Market or Supply Chain).
The facilitators need to focus on device accessibility by providing subsidies for smartphones for marginalized communities and come up with affordable smartphones for education purposes.
Furthermore, there is a strong need for low-cost / subsidized internet for these communities to connect them with the digital world. The school or facilitators also need to focus on spreading awareness about the internet usage and its benefits to students in rural communities because many parents are digital-illiterate and not able to help their children.
Sometimes even if the students and teachers have access to devices and the internet, they still struggle to use the system for teaching and learning purposes because they need strong assistance to use the device and the software at least in the initial days.

Fortunately, all the three facilitators are playing a great role in digitalizing education in rural areas. Many non-profit organizations are tirelessly working to bridge the digital divide by empowering teachers with technology through a blended approach.
The Modi government is also trying hard in this regard. The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), Government of India launched the ‘Digital India’ programme with the vision to transform India into a digitally empowered society and knowledge-based economy by ensuring digital access, digital inclusion, digital empowerment and bridging the digital divide.
To achieve these objectives, particularly in rural, tribal and remote areas, Ministry of Education offers high quality educational programmes through DTH channels as well as web platforms under the aegis of PM e-Vidya.
Some of the major education initiatives are as follows:
– DIKSHA the nation’s digital infrastructure for providing quality e-content for school education in States/UTs and QR coded Energized Textbooks for all grades (one nation, one digital platform). Till date (25.07.2023) DIKSHA has clocked more than 524 crores learning sessions, more than 6,125 crore learning minutes with more than 2.2 crore average daily page hits. A total of 3,17,496 pieces of e-contents are live on DIKSHA as on date.
– 12 DTH Channels in school education and 22 SWAYAM PRABHA channels in higher education are already functional. As per budget announcement for Financial Year 2022-23, the 12 DTH Channels would be expanded to 200 (Two hundred) PM e-Vidya DTH TV Channels.
– SWAYAM (Study Webs of Active-Learning for Young Aspiring Minds) is the national MOOC platform with provision of credit transfer to Universities, for Higher Education Courses. NIOS and NCERT are National Coordinator for school sector courses under SWAYAM, delivering school courses from 9th to 12th. On SWAYAM Portal a total of 10,451 Courses are available out of these courses, 257 courses of NCERT and 431 courses of NIOS are available. For NCERT courses 4.1 lakh students are registered and for NIOS courses more than 34 lakh students are registered.
To realize the vision of Digital India, all efforts related to digital/online/on-air education to enable multi-mode access to education are organized under PM e-Vidya banner as part of Atma Nirbhar Bharat Abhiyaan.